1) ‘Economics is the study of the principles governing the allocation of scarce means among competing ends when the objective of the allocation is to maximize the attainment of the ends.’
a) Draw the production possibility curve and list the underlying assumptions.
b) describe the above statement by referring to your graph for problem (a).
c) describe three fundamental economic problems which reflect the reality of scarce resources.
2) On April 20, 2010, an oil-drilling platform owned by British Petroleum exploded in the Gulf of Mexico, causing oil to leak into the gulf at estimates of 1.5 to 2.5 million gallons per day for well over two months. Due to the oil spill, the government closed over 25 percent of federal waters, which has devastated the commercial fishing industry in the area.
a) Define consumer surplus and producer surplus.
b) Draw a standard supply and demand diagram which relates to the above situation.
c) Using the diagram in (b), describe how the reduction in supply from the reduced fishing waters will either increase or decrease consumer surplus and producer surplus.
3) Suppose the demand and supply curves for eggs in the Malaysia are given by the following equations:
Qd = 100 – 20P, and Qs = 10 + 40P
Where the Qd = millions of dozens of eggs Malaysian would like to buy each year; Qs = millions of dozens Malaysia farms would like to sell each year; and P = price per dozen of eggs.
a) Fill the missing data in the table. Show your workings.
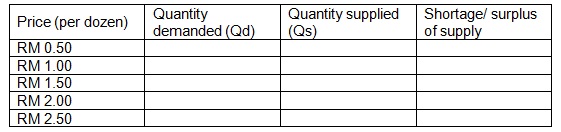
b) Use the information in the table to find the equilibrium price and quantity.
c) Graph the demand and supply curves and identify the equilibrium price and quantity.
4) Fill in the missing amounts in the following table:
a) Fill the missing data in the table. Show your workings.
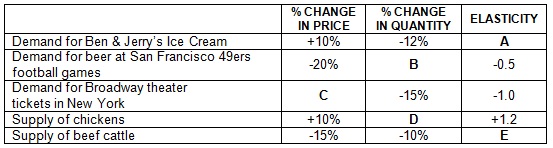
b) Would you recommend that Ben & Jerry’s move forward with a plan to raise prices if the company’s only goal is to increase revenues? describe.
c) Would you recommend that beer stands cut prices to increase revenues at 49ers football games next year? describe.
d) Briefly describe TWO (2) determinants of elasticity other than price of its own.