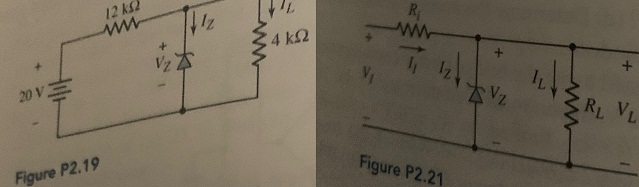
Question 1: In the voltage regulator circuit in Figure P2.21, V1 = 20 V, VZ = 10 V, Ri = 222Ω and Pz(max) = 400 mW. (a) Determine IL, Iz, and IL, if RL = 380Ω. (b) Determine the value of RL, that will establish Pz(max) in the diode. (c) Repeat part (b) if Ri = 175 Ω.
Question 2: A Zeiler diode is connected in a voltage regulator circuit as shown in Figure P2.21. The Zener voltage is Vz = 10 V and the Zener resistance is assumed to be rz = 0. (a) Determine the value of Ri such that the zener diode remains in breakdown if the load current varies from IL = 50 to diode remains in breakdown if the 500 mA and if the input voltage varies from VI = 15 to 20 V. Assume Iz (min) = 0.1/z(max). (b) Determine the power rating required for the Zener diode and the load resistor.
Question 3: Consider the Zener diode circuit in Figure 2.19 in the text. Assume parameter values of Vzo = 5.6 V (diode voltage when lz ≡ 0), rz = 3 Ω, = and Ri = 50Ω. Determine VL, Iz, IL, and the power dissipated in the diode for
(a) Vps = 10 V, RL = ∞; (b) Vps = 10V, RL = 200Ω; (c) Vps = 12 V, RL = ∞; and (d) VPs = 12 V, RL, = 200 Ω.
Question 4: Design a voltage regulator circuit such as shown in Figure P2.21 so that VL= 7.5 V. The Zener diode voltage is Vz = 7.5 V at Iz = 10 mA. The incremental diode resistance is rz = 12 Ω. The nominal supply voltage is Vi = 12 V and the nominal load resistance is RL = 1 kg2. (a) Determine R. (b) If V1 varies by ±10 percent, calculate the source regulation. What is the variation in output voltage? (c) If RL varies over the range of 1 kΩ < RL < ∞, what is the variation in output voltage? Determine the load regulation.
Question 5: A voltage regulator is to have a nominal output voltage of 10 V. The specified Zener diode has a rating of 1 W, has a 10 V drop at 1z = 25 mA, and has a Zener resistance of rz = 5Ω. The input power supply has a nominal value of Vps = 20 V and can vary by ±25 percent. The output load current is to vary between Iz = 5 mA and 20 mA. (a) If the minimum Zener current is to be 17 mA, determine the required R. (b) Determine the maximum variation in output voltage. (c) Determine the percent regulation.
Question 6: Consider the circuit in Figure P2.31. Let Vy = 0. (a) Plot v0 versus vi over the range -10 ≤ vi ≤ + 10 V.(b) Plot i1, over the same input voltage range as part (a).
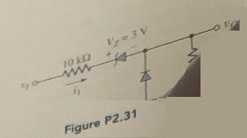
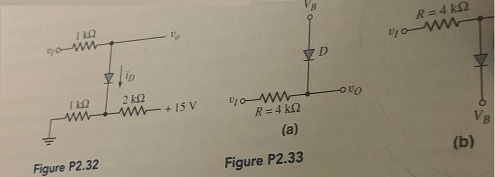
Question 7: For the circuit in Figure P2.32. (a) plot vo versus 0 ≤ vi ≤ 15 v As some Vy = 0.7 V. Indicate all breakpoints. (b) Plot iD over the same range of input voltage. (c) Compare the results of parts (a) and (b) with a computer simulation.
Question 8: Each diode cut-in voltage is 0.7 V for the circuits shown in Figure P2.33. (a) Plot vo versus v1 over the range -5 ≤ v1 ≤ +5 V for the circuit in Figure P2.33(a) for (i) VB = 1.8 V and (ii) VB = -1.8 V. (b) Repeat part (a) for the circuit shown in Figure P2.33(b).
Question 9: The diode in the circuit of Figure P2.34(a) has piecewise linear parameters Vy = 0.7 V and rf =10 Ω (a) Plot vo versus vi for -30 ≤ v1 ≤ 30 V. (b) If the triangular wave, shown in Figure P2.34(b), is applied, plot the output versus time.
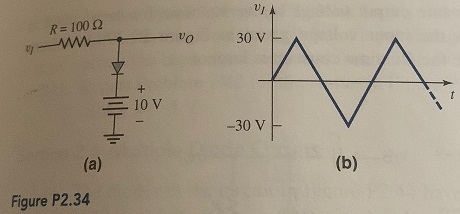
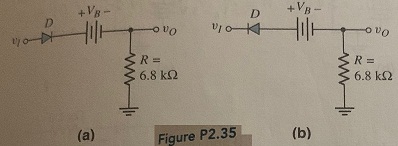
Question 10: Consider the circuits shown in Figure P2.35. Each diode cut-in voltage is Vy = 0.7 V. (a) Plot vo versus v1 over the range -10 ≤ v1 ≤ +10 V for the circuit in Figure P2.35(a) for (i) VB = 5 V and (ii) VB -5 V. (b) Repeat part (a) for the circuit in Figure P2.35(b).
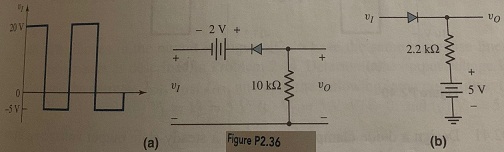
Question 11: Plot vo for each circuit in Figure P2.36 for the input shown. Assume (a) Vy = 0 and (b) Vy = 0.6 V.
Question 12: Consider the parallel clipper circuit in Figure 2.36 in the text. Assume Vz1 = 6 V, Vz, = 4 V, and Vy = 0.7 V for all diodes. For vI = 10 sin ωt, sketch vo versus time over two periods of the input signal.
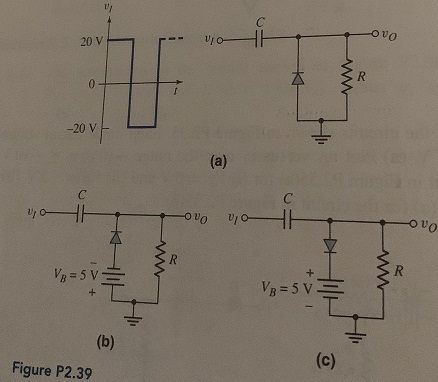
Question 13: Sketch the steady-state output voltage vo versus time for each circuit in Figure P2.39 with the input voltage given in Figure P2.39(a). Assume Vy = 0 and assume the RC time constant is large.